Lambda Invocation Modes
Let's discuss the different ways in which a Lambda function is invoked.
Synchronous Invokes
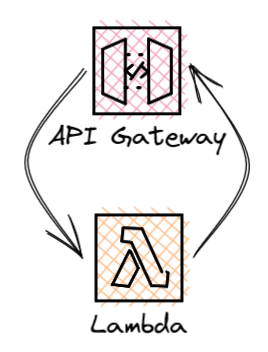
Synchronous invokes are how services like API Gateway integrate with Lambda. The caller, in this case an API, will invoke your Lambda function and wait for a response. The response from the Lambda function is returned back to the caller.
Used In
- API Gateway
- Application Load Balancers
- Amazon Cognito
- Amazon Lex
- Amaxon Alexa
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose
Asynchronous Invokes
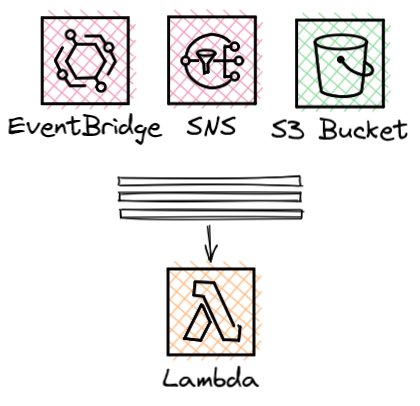
Asynchronous invokes are similar to synchronous invokes in that a caller makes a request directly to Lambda. The request is stored on an internal queue within the Lambda service, meaning the caller recives a fast response and can continue doing other work. The Lambda service then works through the internal queue passing requests to your function code, normally in batches.
If your function returns an error, the Lambda service will automatically retry up to a total of 3 invocations. If after the 3rd invocation there is still a failure the message will either be dropped, or routed a dead letter queue.
It is possible to trace how long a request spends on the queue using the dwell time segment in AWS X-Ray.
Used In
- Amazon SNS
- Amazon S3 Events
- Amazon SES
- AWS CloudFormation
- Amazon CloudWatch Logs
- Amazon Event Bridge
- AWS CodeCommit
- AWS Config
Poll Based Invokes
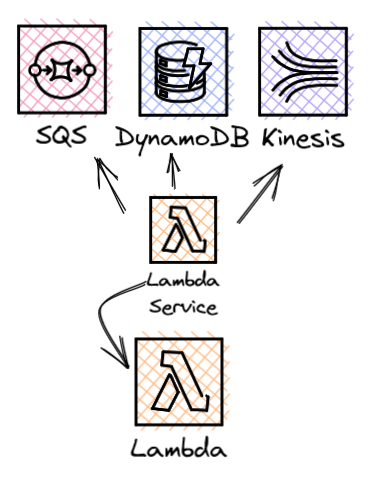
Poll based invokes allow you to integrate your Lambda function with stream or queue based sources without needing to manage the polling yourself. Lambda will poll the service, retrieve records, invoke your function and then manage the communication back to the stream or queue.
It's important to manage error handling when using poll based invokes. For example, if your function takes a message from Amazon SQS and then fails the message will go back on to the queue. Lambda will then pickup the message again, fail again and the message will go back on to the queue. This can happen indefinitely. Ensure you configure the redrive policy on your SQS queue and manage failures within your function code.
Used In
- Amazon DynamoDB steams
- Amazon Kinesis
- Amazon SQS